Would you love to see the most spectacular event of the elk rattle? Then let’s go out. In this article, we look into where and when elk rut occurs and signs that herald the process.
We will look at the best habitats that elk use during this time of the year and then give some guidelines on how one can approach close observation safely and responsibly.
Understanding Elk Rut
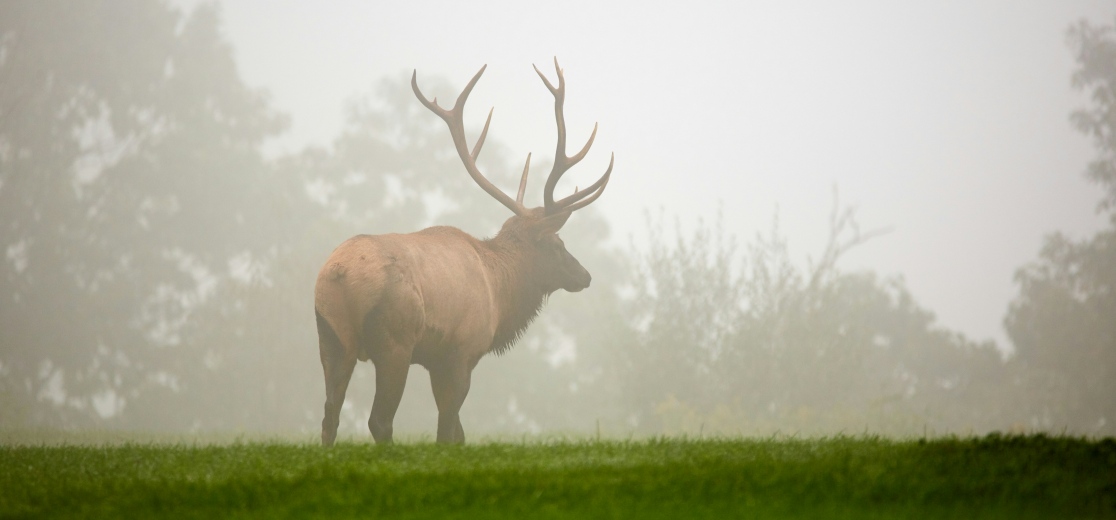
The elk rut is the time of breeding for elk; the tasks involved are that males go on territorial behavior through combat with other bulls to gain exclusive rights to mate with the cows (female elk).
This is a period of large displays including bugling a loud high pitched call used to attract cows and challenge other bulls and bouts of fighting or play fighting with other bulls. Bulls congregate and stand guard over harems of cows to improve their chances of getting the cows pregnant.
When Does Elk Rut Occur?
Elk rut happens from late August to mid-October with the maximum rutting in mid-September. It may take a slightly different time depending on the area and the weather conditions.
The overall idea of a rut is the same across the board: elk and deer get all frisky during their rut, but there are some differences.
Elk rut spends more time on vocalizations like bugling, while deer rut, like the whitetails do more grunts and scraping of scent. The timing and behaviors also vary a little about species and environments.
Factors Influencing the Timing of the Rut
Several factors influence the timing of elk rut, including:
- Photoperiod (Daylight Length): The outburst of rutting behavior is attributed to the shortening of days in late summer and early fall, during the antler formation period.
- Temperature: It is an important factor as the weather becomes cooler elks are better at rutting and thus are more active.
- Food Availability: The condition of reproductive female and their readiness for breeding depends on their nutritional status and due to the lack of foods during some seasons the rut timing is changed.
- Geographic Location: Season and altitude influence the onset of the rut, and if your elk is from Zone 5, located within the Arctic Circle or in the highlands, your peak might be a little earlier than theirs.
- Population Density: Increased population density means that bulls are likely to face greater levels of competition for females and this might result in increased or prolonged rutting – or at least this ought to be the case.
Where Do Elk Go To Rut?
Elk live in the Western states of the United States, Canada, and some parts of Alaska: Colorado, Montana, Wyoming, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington. Eastern populations are fewer in some numbers, sometimes relocated to places like Kentucky or Pennsylvania.
Elk Habitats For Rutting Season
During rutting season, elk typically prefer:
- Mountain Meadows and Open Valleys: These areas are visibility points for bulls for dominance and collection of harems.
- Forest Edges: Elks of course take shelter in forests but remain around the meadows for feeding and breeding purposes.
- Riparian Zones: Areas near streams or rivers are desirable due to their access to water and abundant vegetation.
Looking for these areas where elk most actively stay in and you will have a better chance to shoot.
Elk Movement Patterns During Rutting
When in rutting season, bulls usually migrate from the past summer’s feeding areas to conventional rut sites, which may be alpine meadows or valleys.
The female elk form groups and this makes it easy for bulls to find competition and fight for groups of females.
While Bulls may shift from one group of cows to another or fight other bulls, there is quite a lot of movement during the rut.
How to Track Elk During the Rut?
Signs of Elk Rutting Activity
During the rutting season, elk exhibit distinct behaviors that signal heightened mating activity.
- Bugling: Bull elk produce loud, high-pitched calls known as bugles to attract cows and challenge rival bulls. These calls echo through valleys and meadows, especially during early morning and evening hours.
- Sparring and Fighting: Bulls engage in physical confrontations, locking antlers to establish dominance. This behavior is often accompanied by aggressive posturing and thrashing of antlers against vegetation.
- Harem Formation: Dominant bulls gather and defend harems of cows, displaying protective behavior and chasing off competitors.
- Wallows: Bulls roll in mud wallows scented with their urine to coat themselves in a musky odor, making them more appealing to cows. Wallows are typically found near water sources or muddy patches.
- Scent Marking: Bulls rub their antlers and bodies on trees and shrubs to leave scent marks and physical signs of their presence.
- Increased Movement: Bulls and cows are more active during the rut, often seen moving between feeding areas and traditional rutting grounds.
Tips For Elk Tracking
- Listen for Bugling: Elk are easily spotted in the morning before sunrise and in the evening before it becomes dark. Just creep towards it to make sure they do not run away as a result of sensing your presence.
- Search for Wallows: Stem or fresh patches and tracks in mud which is near water sources. It should also be noted that these areas are prime rutting zones.
- Spot Rubs: Look for trees with stripped bark that are created by rubbing antlers while in rubbing zones. One can recognize fresh rubs have been made by elk recently.
- Look for Tracks and Droppings: To trace activity signs look for trails with big, hoof-like prints and the oval-shaped scats.
- Observe Herd Behavior: Watch individual herds of elk from a distance and if possible use binoculars to help identify the harems that tend to be sighted in meadows or edges of forests.
Best Times of Day for Observing Elk
Elk are mostly on the move in the early morning (immediately after sunrise) and late in the evening (a couple of hours before sunset).
These are the best times to observe rutting behavior since Elk are foraging or mating most often during early morning and at dusk specifically during the cooler periods.
Early morning observations are relatively advantageous due to less disturbance, while evenings offer better visibility of elk moving toward feeding grounds.
Optimal Locations for Observing Elk
- National Parks
- Rocky Mountain National Park(Colorado)
- Yellowstone National Park(Wyoming, Montana, Idaho)
- Grand Teton National Park(Wyoming)
These parks are known for their large elk populations and provide accessible locations for observing rutting behavior in their natural habitats.
- State and National Forests
- San Juan Mountains(Colorado)
- Bitterroot National Forest(Montana/Idaho)
These locations have dense forests and open meadows where elk gather during the rut.
- Wildlife Management Areas (WMAs)
- National Wildlife Refugeslike the Klamath Basin in Oregon and California are excellent spots for viewing elk, especially during the rut.
- Open Valleys and Meadows
- Look for elk in meadows or valleys near forest edges, where they often congregate for mating rituals. The visibility here allows you to observe their movements and behaviors more easily.
Ethical Considerations and Safety Tips
- Keep a Safe Distance
Always view elk from a proper distance, maintaining at least a hundred yards in most cases. According to other hunters, bull elk, particularly during the rut, are not friendly animals and may charge at anyone they see. To catch or even get very close to the animals is to endanger too much pressure that makes them act dangerously.
- Use Binoculars and Scopes
As a result, do not threaten the elk and instead, use binoculars/ spotting scope to view them rather than have close access to them. This in turn helps to limit the interference that you would have on their natural behavior patterns.
- Avoid Disrupting the Rut
Some temperate-adapted breed bulls and cows require freedom to mate and do not meddle with harem establishment or bulls. This is important so that you do not interfere with their routines in any way while studying them.
- Stay Quiet and Stealthy
Elk have well-developed hearing abilities and are easily frightened by noise. Do not shout and do not attempt to physically capture the perpetrator.
- Know Elk Behavior
Being aware of the body signals the elk displays is an advisable way of handling these animals. Bulls may charge (paw the ground, bugle loudly, etc) this is due to overprotecting their territory or the cows. When an elk appears anxious or pays attention to you, that’s the best time to retreat.
- Trail Cameras
If you would like to view elk but avoid getting too close to the animals, install motion-sensitive trail cameras along paths with elk signs. These enable you to make photo or video records of the rut without endangering either the participants or the observers.
- Respect Regulations
Always adhere to the rules and regulations of the park or wildlife reserve regarding such issues as trail use, camping, or visiting certain areas during the mating season.
Conclusion
They witness an amazing display of pure muscle and grace when in the course of the elk rut. If you are wondering when, where, and how these displays occur, anyone can watch this phenomenon responsibly and safely. Always apply the spirit of the law to benefit the elk, ensuring positive memories and experiences.
Learn More About Elks:
- Roosevelt Elk vs Rocky Mountain Elk
- Elk Vs Moose: How To Identify Them?
- Top 10 Caliber For Elk Hunting
- 9 Best States For Elk Hunting You Must Know




















Leave a reply