Have you at some point in your life caught a fish and then thought, “Is this a white crappie or a black crappie?” You’re not the only one! These popular freshwater fish are closely related, but some distinctive characteristics can help you distinguish them. This detailed manual will reveal the mystery of black vs. white crappie. We will study their physical features, where they usually live, and their special behaviors and fishing techniques.
How To Quickly Differentiate White vs Black Crappie?
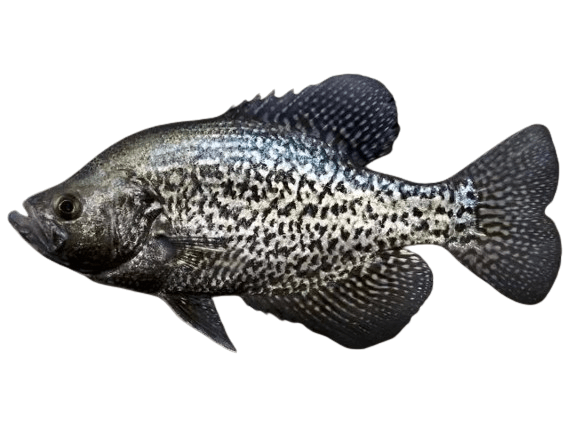

Black Crappie |
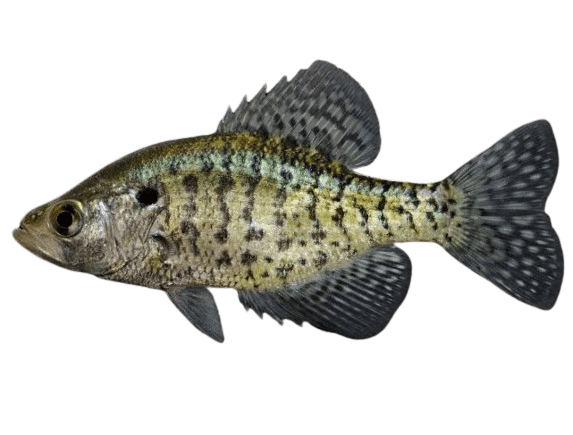

White Crappie |
The easiest way to tell white crappie from black crappie is by their markings:
- Black Crappie: Irregular dark scars all over its body.
- White Crappie: Vertical dark bars running down its body, like stripes.
If the markings are faint, look at the dorsal fin (the spiky fin on the back).
- Black Crappie: Has 7 or 8 spines on its dorsal fin.
- White Crappie: Has 6 or fewer spines on its dorsal fin.
The above ways will tell you how to tell a white crappie from a black crappie in the easiest way. Now let’s look at their differences in detail and get to know these fishes better.
Biological Differences
Although white crappie and black crappie are closely related, some biological differences between them are quite significant. We will now look into their physical features, habitat preferences, and life cycles.
1. Physical Characteristics
- Markings: This is the most remarkable difference. The black crappie has an irregular dark spot pattern all over its silvery body, whereas the white crappie has vertical dark bars on its sides.
- Dorsal Fin: The black crappie has 7-8 spines on its dorsal fin, whereas the white crappie has 5-6.
- Body Shape: Black crappie usually has a deeper body and a shorter, round head than white crappie that is slenderer in build.
- Mouth: The black crappie features a smaller, upside-down mouth that is perfect for surface feeding, while the white crappie has a larger, horizontal mouth for grabbing prey in mid-water.
2. Habitat and Distribution
- Black crappies: The lakes and rivers must be weed-free and have good water quality to be preferred. They’re found in the whole of North America from the Rocky Mountains to the east and Canada.
- White Crappie: Adapting to different water clarity more easily, the black crappie tolerates the murkier waters than the black crappie. Their habitat covers almost the whole of North America.
3. LifeSpan and Growth Rate
- Life Span: Both kinds of fish can live up to 10 years, but, on the other hand, black crappie usually die a little earlier on average.
- Growth Rate: White crappie gets bigger faster than black crappie. The average white crappie can grow to 12-15 inches, while the black crappie can usually be found at 10-12 inches.
4. Other Interesting Facts
- Both species are fish widely used for sports fishing and are appreciated for their gentle taste.
- They are opportunistic feeders, thus eating insects, minnows, and other small fish.
- They can hybridize in places where their habitats overlap.
Behavior Differences
Although both white and black crappie have a lot in common, there are some tiny differences in the way they do their fishy lives. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Feeding Patterns
- Black crappies: These guys are more diurnal feeders, which means they are most active during the day, especially at dusk and dawn. They usually concentrate on the ambush strategy, hiding in the weeds and waiting for the prey to come near them.
- White crappies: They are the more opportunistic feeders, active throughout the day and even at night. They are at ease in the open water by feeding and actively searching for their prey.
2. Diet
It is possible to find some differences in their diets, as both species are opportunistic eaters, but not always. Except for some, they are into insects, minnows, and small fish.
- Black crappie may prefer plankton and small crustaceans to a slightly greater extent.
- White crappie may be a bit more aggressive, sometimes going for the slightly larger prey.
3. Spawning Season
Both are spawned in spring, usually when water temperatures hit the mid-50s to low 60s Fahrenheit (13-16°C). They build similar nests in shallow areas with submerged vegetation.
- Black crappies: In general, they are found in slightly shallow water than the white crappie.
- White crappies: Males might be more aggressive in protecting the nest as compared to black crappie males.
Taste Differences
Here’s the thing about white crappie vs. black crappie taste:
- Subtle Difference: Most people have a hard time telling the difference in taste between white crappie and black crappie when prepared similarly.
- Possible Variations: Some say white crappie might have a slightly sweeter flavor due to their diet containing more minnows, but it’s a subtle difference.
- Preparation Matters: The cooking method and seasonings likely have a bigger impact on the final flavor than the fish species itself.
Nutritional Values
Both white crappie and black crappie are excellent sources of lean protein and healthy fats. Here’s a peek at their nutritional profile (per 3 ounces of cooked fish):
- Calories: Around 100-120
- Protein: Around 20-25 grams
- Fat: Low in fat, around 2-4 grams with most being healthy unsaturated fats
- Vitamins and Minerals: Good source of Vitamin B12, selenium, and phosphorus
White Vs Black Crappie World Record
The world record holders for the biggest white crappie and black crappie are surprisingly close in weight, but the black crappie is leading!
- White Crappie: The all-tackle record for white crappie is the 5-pound and 3-ounce fish that breaks the previous one.
- Black Crappie: The black crappie record is held by a goliath that was caught in 2018 on Richeson Pond, Tennessee, and weighed in at 5 pounds and 8 ounces. That’s a hefty slab!
Fishing Strategies For Crappies
While both white crappie and black crappie share many fishing strategies, there are some tweaks you can make to target each species more effectively.
Locations and Timing
- General: Look for areas with submerged structures like brush piles, weeds, fallen trees, and docks in calm water. Crappies like these areas for cover and ambush feeding.
- Spring: Target shallow areas (2-8 feet deep) with cover as crappie move in to spawn.
- Summer: As the water warms, crappie moves deeper (10-20 feet). Locate them near the structure using sonar.
- Fall: Crappie return to shallower areas to feed before winter.
- Winter: Crappies suspend near deeper structures in lakes or rivers.
White Crappie are more adaptable to water clarity, so you might find them in stained or murky water besides clear lakes. They might roam more freely in open water, so adjust your approach accordingly.
Black Crappie Prefer clear water with good visibility and tend to stay closer to cover elements like weed beds or sunken logs.
Bait and Tackle Advice
- Live Bait: Minnows, crickets, and nightcrawlers are all effective for both crappie species.
- Jigs: Small (1/16 to 1/8 oz) jigs with soft plastic bodies in white, black, or chartreuse colors are great all-rounders.
- Live Bait Rags: Bobbers with minnows or jigs work well for both species, especially in spring and summer.
- Trolling: Effective for covering water and finding suspended crappie in open water. Use small crankbaits or blade baits.
Species-Specific Techniques
White Crappie: Their tendency to roam makes them good candidates for:
- Casting: Cast jigs or small crankbaits around the cover and retrieve slowly.
- Trolling: Effective for covering water in open areas.
Black Crappie: Their preference for tight cover makes techniques like:
- Vertical Jigging: Lower your jig or live bait straight down near the structure and jig it slowly.
- Spider Rigging: This advanced technique uses multiple rods with jigs or minnows spread out behind the boat, ideal for clear, calm water.
FAQs
What Is The Main Difference Between White Crappie And Black Crappie?
It is easy to spot their main difference! White crappie has vertical bars on its body, while black crappie has irregular dark blotches.
How Long Do Crappie Live?
Both white and black crappie can live up to 10 years, although black crappie tends to have a slightly shorter lifespan on average.
Is White Crappie Rare?
Not rare! White crappie is quite common throughout most of North America.
Are Black Or White Crappie Better For Ponds?
Either crappie can be a good choice for ponds. White crappie might be better suited though, as they can tolerate murkier water conditions
Can White Crappie Breed With Black Crappie?
Surprisingly, yes! In areas where their habitats overlap, white crappie and black crappie can interbreed, creating hybrid fish.
What Are The Predators Of The White Crappie?
Watch out for bigger fish! Bass, walleye, catfish, and largemouth bass are all common predators of white crappie.
What Month Is Best For Crappie Fishing?
Spring and Fall are prime crappie fishing times. In spring, they’re near the shallows for spawning. In fall, they’re feeding up before winter.
What Is The Best Crappie Bait?
You can’t go wrong with live bait like minnows or crickets. Small jigs in white, black, or chartreuse colors are also very effective for crappie
How Deep Do You Fish For Crappie?
The depth you fish for crappie depends on the season. In spring, they’re shallow (2-8 feet). In summer/winter, they move deeper (10-20+ feet).
Conclusion
In short, despite the resemblance, white and black crappie are not the same. Markings and fin spines are the ways to distinguish them most obvious and easy. Their habitat preferences and behavior also comprise some changes.
Both are tasty fish, yet, the capture of them involves knowing their seasonal migrations and the baits they like. This manual will assist you in finding and catching the widely known sport fish.



















Leave a reply